Concerns over Solid Fat and Liquid Vegetable Oil
Solid fat is more stable to oxidation and imparts better texture, extended shelf life and flavour to final product. However, excessive intake of saturated fats is likely to be associated with cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome and diabetes. Unlike saturated fat, liquid vegetable oil offers some health benefits, is prone to oxidation and often results in weak texture in food products. Conversion of liquid oils into solid fat by either hydrogenation or interesterification or fractionation has therefore, been adopted by industries to produce fat with required textural characteristics and health benefits. Partial hydrogenation, which is more common in industries, involves addition of hydrogen to oil to make it solid or semisolid. The process is of great health concern as it results in the formation of trans-fatty acids, which have been shown detrimental for heart health in several epidemiological studies. The World Health Organization (WHO) has identified trans-fatty acids (TFA) as a significant public health concern and recommends limiting trans-fat intake to less than 1% of total energy intake.
What Are Oleogels?
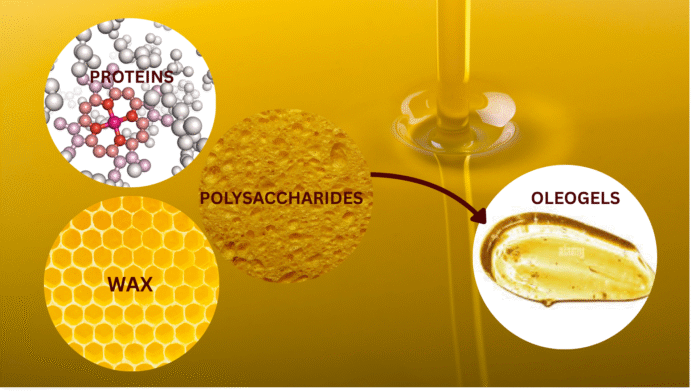
Increased concern over intake of harmful saturated and trans- fat motivated food researchers to find feasible alternatives to replace detrimental fats without compromising texture and flavour of the food products. Out of various alternatives, oleogelation, an innovative approach, seem to be most promising with respect to food properties and health benefits. Oleogelation is a process of making oleogels by physically entrapping liquid vegetable oil into a 3D network of gel with the help of an oleogelator, which can be a protein, polysaccharide or fatty acid depending upon its application in food. The oleogels so formed contain more than 90% oil but function like solid fat. The entrapped oil retain its chemical integrity in contrast to inter-esterification and hydrogenation. Oleogels are being successfully used as solid fat alternative in bakery, confectionary, dairy and meat products with least probability of trans-fat production.
Significance of Oleogels in Health and Disease
Since the use of oleogels allows to replace trans and saturated fats with unsaturated fats, it reduces adipose tissue build-up, LDL cholesterol, and serum triacylglycerol compared to animal fat or industrial margarine. In a human study, consumption of coconut oil in an oleogel reduced blood triglyceride levels compared to conventional oil. Further, Oleogelation can be used for enhancing solubility and therefore improving the bioavailability of nutraceuticals such as β-carotene, docosahexaenoic acid, eicosapentaenoic acid, isoflavone, lycopene and tannins. Oleogels could provide great opportunity to address malnutrition by providing protection to nutrients/ nutraceuticals.
For Further Reading
- Oleogels for development of health-promoting food products
- Production, health implications and applications of oleogels as fat replacer in food system: A review
- Oleogel-Based Systems for the Delivery of Bioactive Compounds in Foods
- Unlocking the potential of oleogels in edible applications and health impacts